
Atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation are both abnormal heart rhythms.
ATRIAL FLUTTER VS SVT PRO
Pro Tip #1: While these appear to be the same, the difference is in the beat. When it first occurs, it is usually associated with a fast heart rate.
ATRIAL FLUTTER VS SVT SERIES
With SVT, that stimulus comes from a rogue myocardial cell that stimulates an erratic atrial contraction or a series of erratic atrial contractions like those found in patient's with atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter.Ītrial fibrillation (also called AFib or AF) is a quivering or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related complications.Ītrial flutter (AFL) is a common abnormal heart rhythm that starts in the atrial chambers of the heart. In this lesson, we'll take a deeper dive into supraventricular tachycardia for the PALS patient, including looking more closely at an example of what it looks like on an ECG and seeing what findings and measurements lead us to our conclusion. It is also highly amenable to curative treatment through elective catheter ablation, which should be considered in all subjects suffering recurrent symptoms and/or hospital admissions.Narrow complex tachycardia, also called supraventricular tachycardia or SVT for short, is caused by some sort of stimulus originating above the patient's ventricles, as opposed to the normal stimulus that's generated by the SA node. This rhythm is especially sensitive to electrical cardioversion at relatively low energies. Atrial flutter has similar stroke risks to AF and the same guidelines for the use of anticoagulation and for considering cardioversion apply. Treatment is to lengthen the refractory time of (delay conduction through) the AV node using similar rate controlling agents as are used in AF, such as B-blockers.

The flutter waves below have one large square between them, and are therefore conducting at 300bpm. This is due to the anatomical route formed by the depolarisation circuit with the right atrium, which is similar in everyone.Ītrial Flutter produces the characteristic ‘saw-toothed’ flutter baseline in lead II which is readily demonstrated through the administration of adenosine, which blocks all conduction through the AV node for a few seconds, allowing only atrial activity to be demonstrated. The refractory time of the AV node usually lets only one out of two of these beats through, and so the ventricular rate is characteristically 150bpm in most humans. Typical atrial flutter is caused by a re-entry circuit within the right atrium, which characteristically depolarises the atria at 300bpm. This can sometimes be mistaken for atrial flutter or sinus rhythm. This is sometimes referred to as fine AF.Īlternatively, the baseline may appear to form p wave like structures at times – so called coarse AF - which reflect fewer circuits of re-entry. The baseline of an AF ECG may show very little in terms of fibrillation waves. This is essential otherwise, ventricular fibrillation would be induced.Īccessory pathways without the long refractory times of the AV node can conduct AF at very high rates into the ventricle and cause sudden death. The diagram shows these re-entry circuits, which depolarise the atria at very high rates, overwhelming the AV node, which only lets through a minority of the impulses it receives (due to its refractory time). The pathophysiology underlying AF is complex, but essentially the arrhythmia is caused by multiple circuits of re-entry (‘feedback loops’) within the atria which lead to multiple foci of automatic depolarisation (competing waves), stimulating the atria to depolarise at very high rates – usually several hundred times per minute. If the baseline of the rhythm strip looks chaotic, with no organised consistent atrial activity visible, AF is confirmed. If the QRS to QRS interval is irregularly irregular, it is likely you are looking at AF.
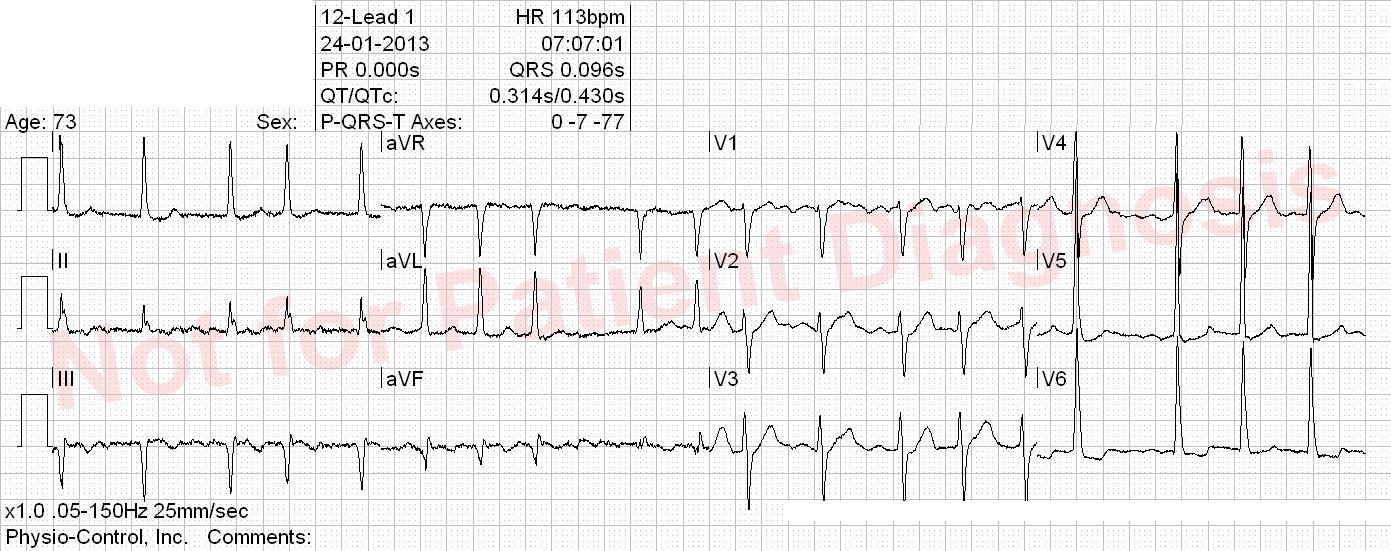
Diagnosis is dependent on correct ECG interpretation and is relatively straightforward.
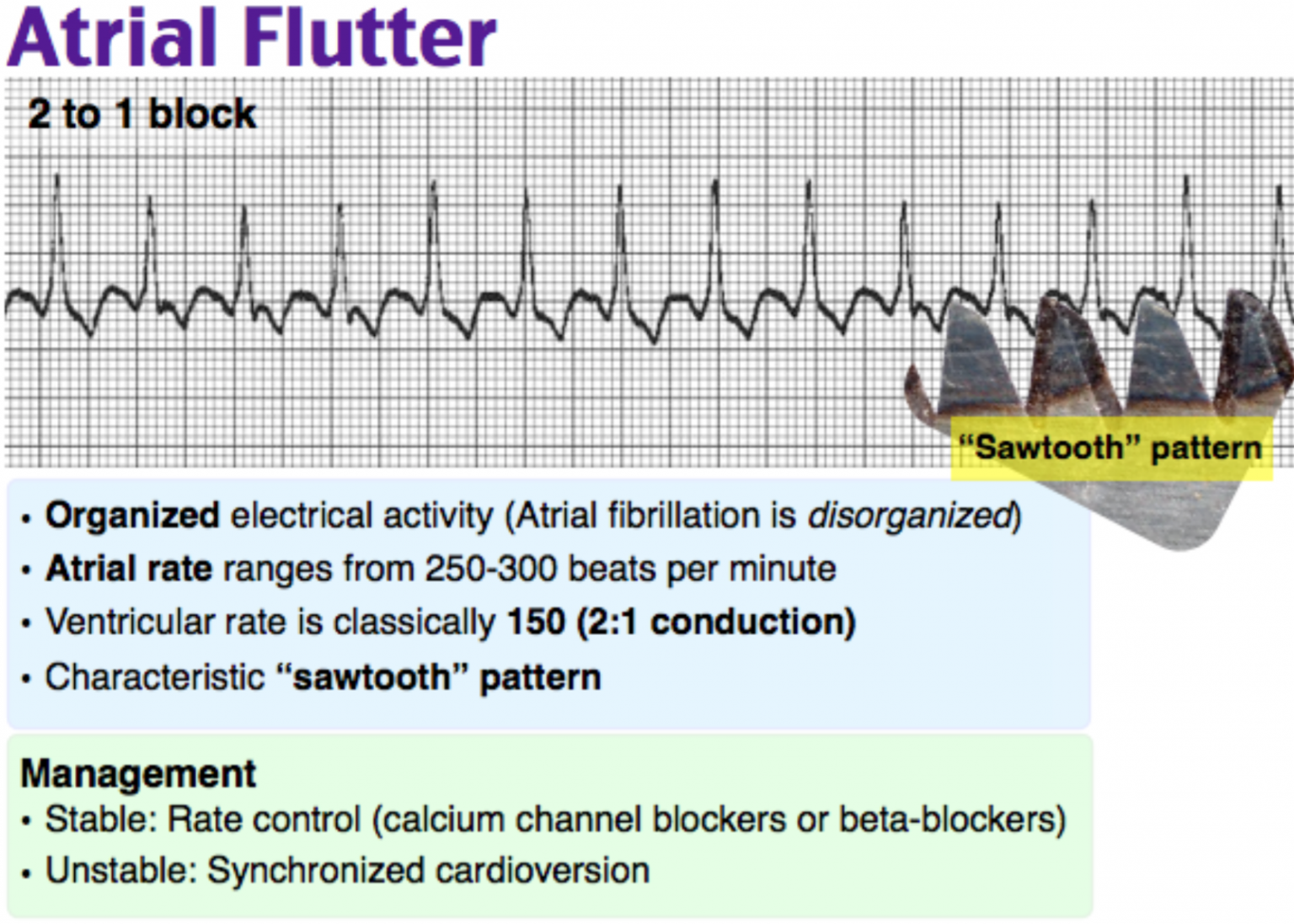
Atrial fibrillation (AF) places a massive burden on the healthcare resources of the United Kingdom as a major cause of stroke, heart failure and hospitalisation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
